
Avoidance, Acceptance, Mitigation, and Transfer. After prioritizing risks, there are four generally accepted responses to these risks:. A risk is generally defined as the probability that an event will occur. Threat and risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing threats and risks. Availability is defined as a characteristic of a resource being accessible to a user, application, or computer system when required. One of the goals of a successful information security program is to ensure integrity or that the information is protected against any unauthorized or accidental changes. Confidentiality deals with keeping information, networks, and systems secure from unauthorized access. CIA (an acronym for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability) refers to the core goals of an information security program. Before starting to secure an environment, a fundamental understanding of the standard concepts of security is needed. Rank the threat level on a scale of 0 through 3 or 0 through 10, where the larger the number indicates the greater the threat. Reproducibility Can the attack be reproduced easily?Įxploitability How much effort and experience are necessary?Īffected users If the attack occurs, how many users will be affected?ĭiscoverability Can the threat be easily discovered? Use DREAD to measure and rank the threats risk level:ĭamage Potential How much damage can be inflicted on our system? The user denies performing a certain action, which could be illegal and harmful.Ī data breach and access to private information occurs, and too much information about a system and its data isĪ service is brought down intentionally or unintentionally resulting in disruptions of applications or services.Ī user gains privilege access greater than that for which he was approved, potentially accessing restricted data or performing restricted tasks. For example, an attacker could masquerade as a legitimate user or an email can be sent under another domain name or email address.Īttackers modify or interfere with legitimate data. Something or someone that pretends to be something that they are not. STRIDE is also a mnemonic tool for security threats it consists of six different categories, as shown in Table 1.1. STRIDE is an acronym for a threat modeling system that originated at Microsoft. At this point, external factors, such as cost or available resources, might affect the priorities. Next, review the specific risks to determine the final order in which to address them. Sorting from high to low provides an easy method to initially prioritize the risks. Then, multiply the likelihood and impact together to generate a total risk score. For example, rank likelihood and impact on a scale from 1 to 5, where 1 equals low likelihood or low probability, and 5 equals high likelihood or high impact. 
One easy way to calculate a total risk score is to assign numeric values to the likelihood and impact. Certain threats might not warrant any action when comparing the risk posed by the threat with the resulting mitigation costs. The rating process weighs the probability of the threat against the damage that could result should an attack occur. Prioritize and address the most significant threats first. Document each threat using a common threat template that shows the attributes of each threat.

By examining the current architecture, system, applications, and potential vulnerabilities, identify the threats that could affect the systems and applications.ĭocument the threats.

Break down the architecture of the systems and application, including the underlying network and host infrastructure design, security profiles, implementation, as well as the deployment configuration of the systems and applications. Documentation should include a system, trust boundaries, and data flow.ĭecompose the security components and applications. Gather simple diagrams and related information that show how the systems are connected, both physically and logically. Identify the valuable assets that the systems must protect.Ĭreate an architecture overview. The steps to perform threat modeling are: In addition, the infrastructure, system, or solution is always changing, and new threats are found. The reason for multiple passes is that it is impossible to identify all of the possible threats in a single pass. Threat modeling is an iterative process it should be started when designing a system or solution and should be performed throughout the system or solution lifecycle. It addresses the top threats that have the greatest potential impact to an organization.
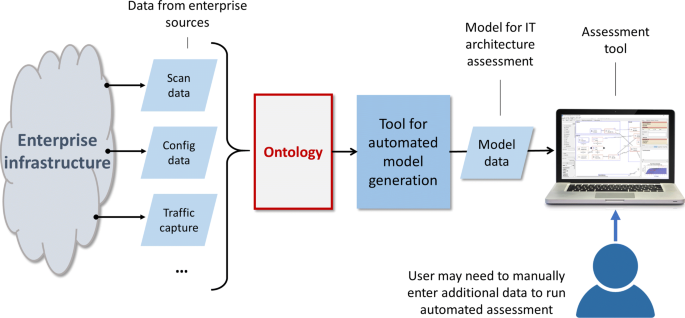
Threat modeling is a procedure for optimizing network security by identifying vulnerabilities, identifying their risks, and defining countermeasures to prevent or mitigate the effects of the threats to the system.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
